Cancer 2019

Theme: Scope of Researches in the field of Cancer
The 4th International Conference on Cancer Research is scheduled for March 20-21, 2019 in Amsterdam, Netherlands. This Cancer 2019 conference will be organized around the theme “Scope of Researches in the field of Cancer”. This conference is the best opportunity for those who have centered their focus on the cancer research and want to share it with the rest of the world. Presentations, distribution of information, meetings with current and potential scientists, discussions on new developments and research, and receiving recognition at this event are the main motive of this conference. Renowned speakers all over the globe are welcomed to talk about their researches and developments, and also discuss the latest updates and new techniques for the treatment and surgery involved in oncology are hallmarks of this cancer conference.
1. Cancer Research: Cancer is considered one of the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. New researches are being conducted every day with an intention to prevent it. The cancer canference focuses on novel therapies which can be used to treat cancer. Upcoming technologies with advancements are much more efficient than previous technologies. This oncology conference will provide a platform for researchers to discuss the progress in cancer treatment that could help humankind.
Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
2. Cancer Biology and Genetics: Cancer is the cause of genetic mutations in cells and how they grow in an uncontrolled manner. Genetic mutations drive the growth and spread of cancer cells to other body parts. Tumor interactions with the surrounding environment are vital for the discovery of new cancer treatments. Oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are widely studied to know the cause of cancer.
Cancer Conference | Genetics Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
3. Cancer Diagnosis and Staging: Screening and staging of cancer are very important to prevent the development of cancer in an individual. It could reduce the number of people who develop the disease or reduce the deaths from cancer. It determines the extent to which cancer has developed and spread in the body. TNM Staging, overall staging, whole body imaging are different ways to diagnose cancer. These are widely used and new researches are also being conducted to improve these techniques.
Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
4. Cancer Metastasis: Dispersion of a primary tumor to other parts of the body is known as metastasis. All cancers have the ability to metastasize and cause death. Metastasis generally occurs in the last stage of cancer either via blood or by lymphatic system or both. Most common places for metastasis to occur are the lungs, liver, brain, and bones. Steps involved in metastasis are:
· Local invasion
· Intravasation ( in blood or lymph)
· Extravasation( in new tissue)
· Circulation
· Proliferation
· Angiogenesis
Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
5. Cancer Biomarkers: On association with the mutations these markers offer a quantitative way to determine when an individual is predisposed to a particular type of cancer. Mutations of genes like BRCA1 and BRCA2 are advanced breast cancer biomarkers, and mutations on genes like KRAS, p53, EGFR, erbB2 are used for colorectal, oesophageal, liver, and pancreatic cancer. Each biomarker identified or introduced should be studied in detail to know its exact role in the field of caner.
Cancer Conference | Biomarker Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
6. Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery and Development: Role of drugs to treat cancer involves clinical aspects at an experimental as well as clinical level. Scientists have to establish experimental models and target oriented approaches to adapt to the changes in drug development. Daily researches are done on this just to save people from such disease. The things to be kept in mind while doing the research are cancer drug targets, the molecular study of cancer, biochemical pharmacology, clinical pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics.
Cancer Conference | Anti-cancer Drug Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Clinical Pharmacology Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
7. Precision Cancer Medicine: To either treat existing cancer or to prevent cancer from developing, vaccines are used which are made either from cancer cells or are pure antigens or also from the immune cells of the patient (are specific to the patient only). Clinical trials on such discoveries should be performed to avoid any loss of life at a later stage. Example: HPV vaccine and hepatitis B vaccine prevent cervical cancer and some liver cancers.
Cancer Conference | Cancer Medicine Conference | Clinical Trials Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
8. Cancer Bio-Informatics: An emerging study combining bioinformatics, clinical informatics, information technology, medical informatics, mathematics together, now, address to the clinical challenges in early diagnosis, the predictive prognosis of patients with cancer. The specificity, applicability, integration of methodologies, computational tools, cancer clinical trials data management software, and databases which can be used to explore the molecular mechanisms of cancer and identify and validate network biomarkers, novel biomarkers, and individualized medicine in cancer.
Cancer Conference | Clinical Oncology Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
9. Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy has been found to be a successful method for treating cancer but not in all cases. In some cases, it may even cause death. Its effectiveness depends upon the type and stage of cancer along with the physical fitness of an individual. For more effective results, it is sometimes combined with other therapies or treatments.
Cancer Conference | Chemotherapy Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
10. Imaging and Radiation Therapy: For précised and accurate treatment of cancer, imaging is essential in radiation therapy. Without Imaging the exact position of the tumor cannot be detected especially in the moving organs like lungs. Imaging procedures like MRI and PET scan should be done before performing any treatment.
Cancer Conference | Radiology Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
11. Cancer and Stem Cell Therapy: Stem Cell transplant can treat cancers like leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. Blood stem cells are used to treat leukemia, blood or bone marrow disorders. As stem cells have the ability to differentiate into desired cells and can also be used to treat or prevent any disease or condition. Cancer stem cells, stem cell transplantation, bone marrow transplantation are the techniques used by scientists in treating cancer.
Cancer Conference | Stem Cell Therapy Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
12. Cancer: Psychological and Social Aspects: If one is fighting cancer, it is common to experience psychological distress. Whether it is coping with the diagnosis, the challenges of treatment, or continued worry about a recurrence, such mutations could be difficult to handle. Cancer effects are far more than other diseases. Many survivors find that cancer’s impact spills over into the emotional, psychological and spiritual realms. This might happen either during or right after treatment or not for years.
Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
13. Organ Defined Cancers: Cancer does not affect any organ specifically. It starts at one point and spreads to the other parts of the body. But cancers are generally described by the organ where it originated. To avoid any kind of confusion, cancers can additionally be classified by the type of cell from where the tumor cell originated. The type of cancer a person has needed to be known properly as different types of cancer can behave very differently and respond to different treatments.
Below are the major types of cancer: Breast Cancer, Gynecologic Cancers -Cervical Cancer, Uterus Cancer, Ovarian Cancer, Vulvar Cancer, Brain Cancer, Bone Cancer, Prostate Cancer, Lung Cancer, Lymphoma, Leukaemia, Liver Cancer, Blood Cancer, Eye Cancer, Skin Cancer etc.
Lung Cancer Conference | Hematology Conference | Leukemia Conference | Cancer Conference | Breast Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
14. Pediatric oncology: Branch of medicine concerning childhood cancer is known as pediatric oncology. An arbitrarily adopted standard age for such cancer is 0-14 years but sometimes may include adolescents between 15-19 years. Children are at a risk of developing various cognitive or learning problems due to recurrent chemotherapies or radiotherapies. Most common types of childhood cancers are leukemia (32%), brain tumors (18%) and lymphoma (11%).
Cancer Conference | Pediatric Oncology Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
15. Neuro-Oncology: Neuro-oncology deals with the brain and spinal cord neoplasm which may or are very hazardous and life-threatening. Cancer spreads to the Nervous System either by direct invasion or compression from contiguous tissues. Untreated survival usually amounts to only a few months, and survival with current radiation and chemotherapy treatments may extend that time from around a year to a year and a half, possibly two or more, depending on the patient's condition, immune function, treatments used. Surgery may in some cases be curative, but, as a general rule, malignant brain cancers tend to regenerate and emerge from remission easily, especially highly malignant cases.
· Genetic and Non-genetic factors
· Mechanisms
· Diagnosis and Treatment
· Peri- Tumoral Factors
· Specific Tumors
· Metastatic Tumors
· Initial Patient Evaluation & Care
· Diagnostic Procedures
· Radiotherapy
· Chemotherapy
· Pain & Terminal Care
Cancer Conference | Neuro-Oncology Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
16. Oncology Nursing: Nursing a Cancer patient is not easy. As they have to be emotionally stable to help the patient and their family to cope with the treatment processes or even death in the case. Proper education and training are given so that they can monitor their patient’s progress. Only certified nurses are allowed to take care of these patients. They should know how to handle the side effects of chemotherapy or any other therapy. They should be given advanced knowledge about everything related to cancer.
Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
17. Cancer: Lifestyle and Nutrition: Being a multifactorial disease, Environment (along with Genes) is also responsible for causing cancer. Over the last 25 years, Science has shown that diet, physical activity and body weight are responsible for developing certain cancers. Being overweight or obese is a major risk. Not all but most of the Cancers can be prevented through lifestyle changes. The main risk factors for cancer mortality are related to diet and physical inactivity, use of addictive substances, exposure to air pollution or the use of contaminated needles. The body’s ability to resist cancer may be helped by following a healthy diet, staying physically active, and avoiding excess body fat. Cancer and cancer treatments like chemotherapy can also affect your body's ability to tolerate certain foods and use nutrients.
Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
18. Environmental Exposure and Cancer Prevention: Certain substances present in the environment alter the way our cells function by causing changes in our genes. Some occur naturally (during the process of cell division) but in some cases, DNA damage is the result of environmental exposures. These exposures may include substances, such as the chemicals in tobacco smoke, or radiation, such as ultraviolet rays from the sun. Cancer can be prevented by avoiding prolonged exposure to such radiations.
Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
19. Cancer Awareness and Survival: Increased awareness improves survival. Cancer symptom awareness and cancer survival are associated. Cancer Awareness Program is conducted by government and many organizations to bring the awareness to the people to decrease the cancer levels. Campaigns should focus on improving awareness about cancer symptoms, especially in socioeconomically deprived areas as Social and Economic Impact also harm the quality of cancer care.
Cancer Awareness Conference | Cancer Conference | Global Cancer Conference | Cancer Meeting | Cancer 2019 | Cancer Research 2019 | European Cancer Conference | Oncology Conference | Global Oncology Conference | Oncology Meeting | Oncology 2019 | European Oncology Conference
Cancer happens to be a leading worldwide problem, with ∼14 million recorded new cases every year. In the USA, for example, over 0.5 million people die from cancer every year, making cancer the 2nd cause of death.
Important is the fact that the cancer prevalence has been increasing mostly due to the increased lifespan of people. While recent changes in lifestyle have an impact on the spread of cancer, about two-thirds of the increase in the rate of cancer is due to longevity. More than three-quarters of all people diagnosed with cancer in the UK are over the age of 60.
Adding to the increasing cancer prevalence, there are several reasons that currently lead to an increase in the cancer therapy market. These include the availability and high development cost of better immunotherapy agents, the non-curable and lethal nature of most of the cancer forms, the reduced competition among agents as the use of an agent does not preclude from the concurrent/subsequent use of another one, that cheaper generics are often not considered as available alternatives to newer more costly agents but they are replaced by them, the earlier diagnoses and increased chronic management, the lack of magnitude threshold of drug benefit and increased insurance premiums due to unpredictable disease status. Between the years 2007 and 2013 for instance, the global cancer therapy market more than doubled, the global cancer therapy market increased from $40.0 billion in 2007 to an estimated $47.3 billion by the end of 2008 and $110.6 billion in 2013 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.5%.
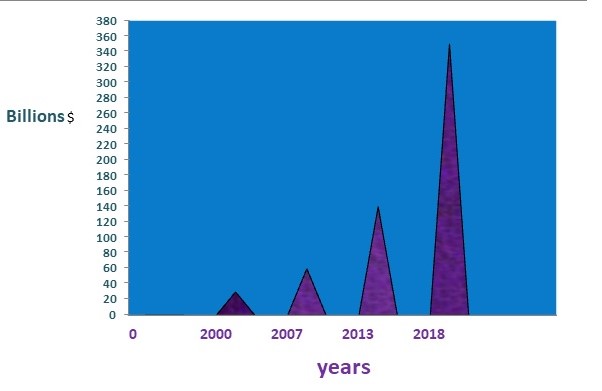
Figure 1: Cancer drug market approach after 2000
This is a high annual growth rate of over 18%. Looking at the targeted therapy separately, which constitutes 45% of the cancer therapy market, this about tripled in within the same duration, increasing from combined market cost value of about $22 billion to almost 70 billion.
The total worldwide cancer drug market approached $14.8 billion in 2000.
Growing at an average annual rate (AAGR) of 12.5%, this market exceeded $26.7 billion in 2005.
Established product lines currently constitute nearly 90% of the global market, but will grow at only a rate of 6.6% AAGR through the period.
Innovative therapies, climbing at an AAGR of 40.2%, reached $8.6 billion in 2005, representing 32% of the total market.
Breast cancer therapy has the largest market with around $11.0 billion in sales in 2007. It increased to $12.0 billion in 2008 and $26.5 billion in 2013, by a CAGR of 16.4%.
Target therapy dominated in 2007 with a 45% share of the total cancer therapy market. This increased to 48% in 2008 and 62.5% in 2013.
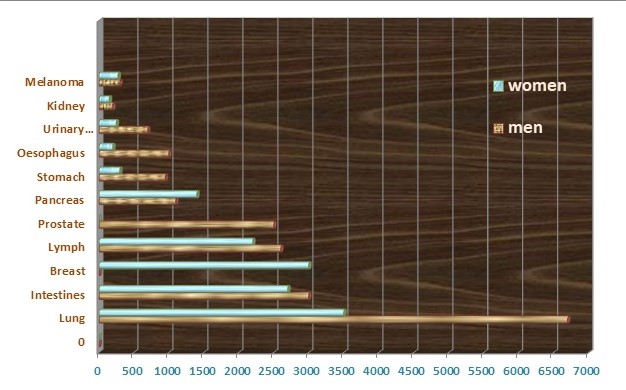
Figure 2: Average number of people suffering from a particular cancer type
There are ethical issues surrounding the comparative research on newer therapies for a dangerous disease like cancer, particularly the prospective research, which generally stems from the fact that exposing study participants to increased risk with experimental therapies may not actually be counterbalanced by clinical benefit. In comparative research, participants may, for example, be harmed by receiving a placebo instead of an active treatment or, more commonly, participants stand the chance of receiving an experimental cancer therapy that will eventually turn out to be inferior to the best usual therapy available to patients. This is ethically problematic, given the recognized ethical principle that patients should receive the best-proven standard of care whenever feasible.
Target Audience:
- Oncologists
- Radiologists
- Students (Any Graduate)
- Oncology Associations & Societies
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Haematologists
- Academicians
- Research Scholars
- Medical Devices Companies
- Biomedical Companies
- Biotechnology Companies
- Surgeons
- Medicine
- Immunologists
- Pharmacists
- Geneticists
- Diagnostic Companies
- Organ Defined Cancers
- Pediatric Oncology
- Oncology Nursing
- Cancer Metastasis
- Cancer Biomarkers
- Precision Cancer Medicine
- Cancer Bio-Informatics
- Chemotherapy
- Imaging and Radiation Therapy
- Cancer and Stem Cell Therapy
- Neuro-Oncology
- Cancer Awareness and Survival
- Journal of Clinical & Experimental Oncology
4 Organizing Committee Members
6 Renowned Speakers
Amal Fawzy
Cairo University, Egypt
Egypt
Dejan Kristic
University of Nish, Serbia
Serbia
Nikola Trifunovic
GeoInstitut, Serbia
Serbia
Dragan Jedvic
Private Madical Practice, Asrocite, Serbia
Serbia
Christine Boer-Doers
Cancer-Med,The Netherlands
Netherlands
Cheng Wang
Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, USA
USA