Glycobiology 2018
Theme: Recent advancements and trends in Glycobiology and Human Physiology
Meetings International feels great pleasure to invite all the participants across the globe to attend the “International Conference on Glycobiology and Human Physiology” during October 24-25, 2018 at London, UK.
International Conference on Glycobiology focuses on the structure, biosynthesis, and biology of saccharides (sugar chains). Human Physiology deals with the functioning of organs and cells in the body. This Conference will provide a suitable platform for scientists, world-class professors, glycobiologists, biochemists, researchers, industry experts, delegates, sponsors and exhibitors from all over the world to discuss recent advancements in Glycobiology and research in the field of Human Physiology. This comprises of proficient keynote presentations, verbal speeches, productive poster presentations and exhibitions. Glycobiology Conferences covers all the comprehensive sessions related to glycobiology, glycoproteomics analysis, glycoimmunology, glycopathology and physiology.
Various members from all around the globe have focused their research and expertise on learning more and more about various biomolecules and use of Glycobiology. This is a best opportunity to meet the global participants in the wider arena of Biochemistry and Glycobiology, to share information, meeting with current and expert researchers and receive name recognition in this two-day premier event.
Target Attendees:
- Glycobiologists
- Scientists and Researchers
- Biochemistry Associations and Societies
- Biochemists
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Biochemistry Experts
- Medical Colleges
- Research Training Institutes
- Pharma Companies
- Professors
- Students
Session 1: Glycobiology and Glycochemistry
Glycobiology and Glycochemistry deal with various aspects of glycan’s, including carbohydrate structure, biochemistry, biological functions and applications.Sugars or saccharides are essential components of all living things and aspects of the various roles they play in biology are researched in various biochemical, medical and biotechnological fields. Sugars are the major contributors in nature. Many natural products contain oligosaccharides that are important for their biological and biochemical activity. Carbohydrates have major roles in a wide range of biological processes including signal transduction mechanisms and immune responses.
Glycobiology Conference| Glycochemistry Conference| Glycobiology and Glycochemistry Conference| Glycobiology and Glycochemistry Congress| Glycobiology workshop| Glycochemistry Workshop| Glycobiology and Glycochemistry Workshop| Glycobiology and Glycochemistry Meeting| Glycobiology Meeting| Glycochemistry meetings
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association , European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy , The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 2: Glycoproteomics Analysis
Glycoproteomics focuses on the role of protein glycosylation in various biological processes. They identify and characterize proteins containing carbohydrates as a post-translational modification. Mass spectrometry is commonly and widely used to identify the sugar moieties attached. Proteomics studies along with glycans produce large volumes of raw experimental data and inferred biological results. Experimental study of proteomics data focuses on freely-available, centralized data resources that store experimental mass spectrometry data and results.
Glycoproteomics Conference| Glycoproteomics Meeting| Proteomics Conference| Proteomics Workshop| Glycans Conference| Glycoproteomics Workshop| Glycoproteomics Symposium | Glycoproteomics Congress
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association , European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy , The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 3: Glycoimmunology
Carbohydrates were essential in the early history of immunology in depicting the identity of antigens which are recognized by antibodies. The capacity of these antibodies to recognize glycans and carbohydrate related molecules was exploited in studies defining the size of the antigen-binding site. Various carbohydrate-binding proteins, or lectins, have been identified on the surfaces of immune cells which intensify the significance of carbohydrates in both innate and adaptive immune responses in development of modern vaccines and immunological therapeutics. Recently glycobiologists and immunologists are now collaborating to explore this crucial field in the area of immunobiology
Glycoimmunology Conference| Immunology Conference| Glycoimmunology Meeting| Glycoimmunology Workshop| Glycoimmunology Symposium| Glycoimmunology Congress
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 4: Glycans in Diseases and Therapeutics
Glycomedicine plays the significant role in cell-cell adhesion i.e. a technique utilized by cells of the immune system by means of sugar-binding proteins called lectins, which distinguishes specific carbohydrate moieties. Glycans are the building blocks of carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids. Glycans play significant roles in many biological phenomena and various pathophysiological processes. .The roles of glycans and glycoconjugates in cancer have been emphasized. A small alteration in glycosylation can hugely regulate the entire pathway and mechanisms of cancer, which leads to an indication as a biomarker development leading to various therapeutics development in cancer research.
Glycomedicine Conference| Cancer Conference| Glycomedicine Workshop| Glycans in Diseases and Therapeutic Conference| Glycans in Diseases Workshop
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 5: Glycolipids and Glycopeptides
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic bond or covalent bond. They maintain the stability of the cell membrane and facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. They are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment.
Glycopeptides contain carbohydrate moieties (glycans) that are covalently attached to the side chains of the amino acid residues that constitute the peptide.
Glycolipids and Glycopeptides Conference| Glycolipids Conference| Glycopeptides Conference| Glycolipids and Glycopeptides Workshop| Glycolipids and Glycopeptides Symposium| Glycolipids and Glycopeptides Congress
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 6: Mass Spectrometry Analysis
Mass Spectrometry Analysis is a technique that ionizes chemical species and sorts the ions according to their mass-to-charge ratio. It is used for characterization and elucidation of glycan structures. A mass spectrum is a plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio during experimental analysis. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) and fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry (FAB-MS) may be used to detect intact glycans. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) also provides good signals for the smaller glycans. Various free and commercial software are now available which interpret MS data and help in Glycan structure characterization.
Mass Spectrometry Analysis Conference| Mass Spectrometry Analysis Workshop| Mass Spectrometry Analysis Meeting| Mass Spectrometry Analysis Symposium| Mass Spectrometry Congress
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 7: Glycans in Vaccine Development
Recently, the interest in exploiting the biological activity of glycans as vaccine components has considerably increased. On the one hand, carbohydrates display epitopes to generate protective antibodies against pathogen-derived cell wall structures and on the other hand, glycans have the potential to stimulate the immune system. So, they can act as potent vaccine adjuvants. An effective vaccine consists of two major components, the vaccine antigen and an adjuvant. The vaccine antigen is an original or modified part of the pathogen that causes the disease. The response activated by vaccination should induce antigen-specific plasma cells secreting protective antibodies as well as the development of memory T and B cells. Carbohydrate structures on pathogens represent an important class of antigens that can activate B cells to produce protective anti-carbohydrate antibodies in adults.
Glycans in Vaccine Development Conference| Glycans in Vaccine Development Meeting| Vaccine Development Conference| Glycans Conference| Glycans in Vaccine Development Symposium
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 8: Glycoconjugates, Glycomics and Metabolomics
Glycoconjugates are carbohydrates that are covalently connected to other biological molecules, for example, amino acids (to generate peptidoglycans), proteins (glycopeptides and glycoproteins), lipids (glycolipids and lipopolysaccharides), and other small molecules (glycosides). They are formed by glycosylation process. Glycoconjugates are composed of many different categories, for example, glycoproteins, glycopeptides, glycolipids, peptidoglycans, glycosides and lipopolysaccharides.
Glycomics is a subset of the field of glycobiology that intends to recognize the structure and capacity of the total arrangement of glycans (the glycome) produced in a given cell or living being and identify all the genes that encode glycoproteins.
Metabolomics has experienced a fast innovative advancement in the previous two decades. These advances have prompted the utilization of metabolomics for identifying new biomarkers or elucidate disease mechanism
Glycoconjugates Conference| Glycomics Conference| Metabolomics Conference| Glycoconjugates, Glycomics and Metabolomics Conference| Glycoconjugates Workshop |Glycoconjugates, Glycomics and Metabolomics Congress
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society
Session 9: Glycoscience and Monosaccharides
Glycoscience involves an extensive scope of learning and research carbohydrate metabolism, structure, anabolism and function. Glycans are expressed in all microorganisms, including prions, as well as in all higher organisms, thus it is not surprising that their biological and disease impacts are profound. New innovations in the field, along with novel perspectives and insights, are helping to shape the future of glycoscience toward a more rationally integrated discipline alongside other biological and clinical disciplines as glycoscience becomes a cornerstone of modern chemical, biological, and biomedical sciences.
Monosaccharides consist of one sugar unit that cannot be further broken down into simpler sugars. They are also called simple sugars. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose and galactose.
Glycoscience and Monosaccharides Conference| Glcoscience Conference| Monosaccharides Conference| Glycoscience and Monosaccharides Workshop| Glycoscience and Monosaccharides Symposium| Glycoscience and Monosaccharides Congress
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society.
Session 10: Recent advances in Glycobiology
Glycans are essential components of numerous biotherapeutic agents, varying from natural products to molecules based on various rational designs to recombinant glycoconjugates and glycoproteins. The glycan components of these agents can be important determinants of their biological activity and therapeutic efficacy. Modern patenting of new therapeutics commonly requires clarifications of the composition of matter in the claimed molecule for approval. Various remarkable advances can be found in the areas of imaging, structure prediction technologies and advancement of hybrid methods to understand the structure and function of carbohydrates and proteins.
Recent advances in Glycobiology Conference| Recent advances in Glycobiology Workshop| Recent advances in Glycobiology Symposium| Recent advances in Glycobiology Congress
Related associations:
European Proteomic Association, European Society of Gene and cell therapy, Human Proteome Organization, British Society of Gene Therapy, The International Centre for and Biotechnology, Australasian Proteomics Society, New Zealand Mass Spectrometry Society.
Session 11: Respiratory System
Respiratory illnesses, regardless of whether acute or chronic, communicable or noncommunicable, impose a major global burden and influence a large number of individuals. Due to the progress in investigational technologies (such as imaging and biomarkers), respiratory diseases can be diagnosed and managed more efficiently. Techniques such as real-time MRI, three-dimensional ultrasonographic computing and ‘visiology’ are extending our comprehension of a range of conditions. So-called ‘biological’ approaches are increasingly prominent in respiratory medicine, and new devices for ventilatory support or endoscopic procedures are constantly becoming available.
Respiratory system Conference| Respiratory Disease Conference| Respiratory Diseases Workshop| Respiratory Diseases Congress
Related associations:
European Respiratory Society, American Association for Respiratory Care, Respiratory Health Association, American Physiological Society, British Medical Association
Session 12: Digestive System
This Conference focuses on the current advances in the diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive modalities of digestive diseases based on the latest research. There are several different technologies and innovations that can be used to diagnose and treat digestive diseases. Some of the commonly used diagnostic technologies are:
- Colonoscopy
- Sigmoidoscopy
- Esophageal Manometry
- Upper GI Series
- Anoscopy
Digestive System Conference| Digestive Diseases Conference| Digestive Diseases Congress| Digestive Diseases Workshop| Digestive Diseases Symposium
Related associations:
American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, American Gastroenterological Association
Session 13: Endocrine System
Several advances in the management of endocrine diseases can be seen in the recent years. These include novel drugs developed as a consequence of better understanding of the pathophysiology of endocrine conditions, as well as improved delivery methods for existing drugs. Control of hormone hypersecretion and replacement of hormone deficiencies are the mainstay of treatment in endocrinology. The ultimate goal of treatment is to reduce the long-term morbidity and mortality associated with hormone hypo- or hypersecretion and to improve the quality of life
Endocrine System Conference| Endocrine Diseases Conference| Endocrine Diseases Workshop| Endocrine Diseases Symposium
Related associations:
American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists
Session 14: Reproductive System
Many kinds of research are going on to prevent and cure reproductive disorders. In vitro fertilisation is a type of assisted reproductive technology used in case of infertility. Sexually transmitted diseases are caused by unprotected sex. Recent research focuses on the treatment and prevention of various reproductive disorders such as infertility, endometriosis, sexually transmitted disease, cervical cancer, etc.
Reproductive System Conference| Disorders of the Reproductive System Workshop| Reproductive & Sexual Health Conference| Human Physiology Conference
Related associations:
American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, Association of Reproductive Health Professionals
Session 15: Urinary System
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. Urinary system eliminates waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. Urinary tract infections affect millions of people every year.
Urinary System Conference| Urinary tract infections Conference| Urinary System Workshop
Related associations:
American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, American Urological Association
Session 16: Nervous System
The nervous system conducts stimuli from sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord and the brain and spinal cord conducts impulses back to other parts of the body. The nervous system consists of Central nervous system and Peripheral nervous system. The Central nervous system includes brain and spinal cord. The Peripheral nervous system includes the Somatic and the Autonomic nervous systems. The development of gene therapy for nervous system tumours has progressed rapidly and may be prototypical in the development of therapies for inherited and acquired disorders of the nervous system.
Nervous System Conference| Nervous System Disorders Conference| Nervous System Workshop| Nervous System Symposium| Human Physiology Conference
Related associations:
American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, American Society for Neurochemistry
Session 17: Cardiovascular Physiology
The essential components of the cardiovascular system are the heart, blood and blood vessels. It transports oxygen and nutrients to the cells of the body in order to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilize temperature and pH, and maintain homeostasis. Pulmonary Circulation carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the lungs, and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. Systemic Circulation carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
Cardiovascular Physiology Conference| Cardiovascular Disorders Conference| Cardiovascular Disorders Workshop| Cardiovascular Physiology Symposium| Cardiovascular Physiology Congress
Related associations:
American Heart Association, American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, Human Anatomy and Physiology Society
Session 18: Bones and Joints
Bones are mineralized dense connective tissues made up of few cells in mineralized matrix. It consists of 30-40% of our body weight. It is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeletal system. Joint is a junction between two or more bones or cartilages. It may be movable or immovable. The human skeleton can be divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton is formed by the vertebral column, the skull, the rib cage and other associated bones. The appendicular skeleton consists of the pelvic girdle, the shoulder girdle and the bones of the upper and lower limbs.
Bones and Joints Conference| Bones and Joints Congress| Orthopaedics Conference| Bones and Joints Symposium
Related associations:
American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, Australian Orthopaedic Association
Session 19: Integumentary System
The integumentary System comprises of the skin and its adornment structures including hair, nails and organs and in addition veins, muscles and nerves. The skin covers the body and is the biggest organ of our body. Normal maladies and wounds to the skin incorporate Rashes, Blister, Infection, Sunburn, and Skin Cancer and so on.
Functions of the skin:
- Regulation of body temperature
- Protection
- Cutaneous sensations
- Excretion and absorption
- Synthesis of Vitamin D
Integumentary System Conference| Integumentary System Congress| Integumentary System Symposium| Integumentary System Workshop| Integumentary System Meeting
Related associations:
American Physiological Society, British Medical Association, Royal Society of Medicine, Brazilian Medical Association, Human Anatomy and Physiology Society
Market Research
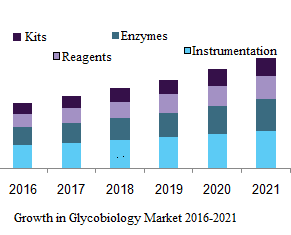
Global Glycomics /glycobiology market was valued at US$ 657.3 million in 2016, and is expected to reach US$ 1,891.9 million by 2025, expanding at a CAGR of 12.4% from 2017 to 2025.
Glycobiology has a wide range of applicability; but for the purpose of the study, this market is categorized as diagnostics, drug discovery & development, oncology, immunology other applications. It is studied that, in the base year 2016 drug discovery & development was major revenue generating segment because increase in R&D activities for the development of novel therapies and higher number of unmet needs are primarily driving the market growth.
Geographically, the Glycomics market is dominated by North America, followed by Europe, Asia, and the Rest of the World (RoW). Growth in the Asia segment is primarily driven by the increasing demand for the personalized medicine and commercialization of pharmaceutical and biotechnology research.
The market is observed to be highly competitive and comprises large number of players. However, the market is currently dominated by few players such as Agilent Technologies, Bruker Corporation, Danaher Corporation, Merck KGaA, New England Biolabs, Prozyme, Inc., R&D Systems, Inc., Shimadzu Corporation, Takara Bio, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waters Corporation and others.
Rising investments in research by the government along with escalating focus of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies on novel drug development are other major factors contributing toward growth of the sector. For instance, in February 2015, the government of Canada announced the federal funding of around USD 27.3 million for a national research network, namely GlycoNet, to develop new vaccines and drugs for various medical conditions, including genetic diseases, influenza, and diabetes.
The U.S., Germany, U.K., France, Japan, China, and India are projected to account for the highest application of glycomics. Availability of glycobiology products in these countries along with the presence of a large number of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies in these countries is expected to contribute toward growth.
About City
London is the capital and most populous city of England and the United Kingdom. It is a leading global city in the education, arts, commerce, finance, healthcare, entertainment, research and development, fashion, media, professional services, tourism and transportation. It is the world's most-visited city as estimated by international arrivals and has the world’s largest city airport system measured by passenger traffic. London's universities form the largest concentration of higher education institutes in Europe. London has a temperate oceanic climate, with warm summers and cool but not cold winters. During October, London will have a fairly cool temperature.
Top Universities in UK:
- University of Liverpool
- Oxford Glycobiology Institute
- Imperial College London
- University of Southampton
- Oxford Brookes University
- Bangor University
- The Open University
- University of York
- Newcastle University
- National Institute for Bioprocessing Research & Training
- The University of Manchester
- University of Cambridge
- University of Westminster
- King's College London
- Bioprocessing Technology Institute
- The University of Glasgow
- University of Bristol
- University of Huddersfield
- Lancaster University
Top Universities in USA:
- Georgetown University
- University of California
- University of Colorado Boulder
- Columbia University
- Yale University
- Duke University
- Dartmouth University
- University of South California
- Case Western Reserve University
- Stanford University
Top Universities in Europe:
- University of Bristol
- University of Zurich
- University of Lausanne
- University of Copenhagen
- University of Oslo
- University of Gothenburg
- Maastricht University
- University of Vienna
- King’s College London
- University of Groningen
- Erasmus University Rotterdam
Top Universities in Asia:
- University of Singapore (NUS)
- Hong Kong University of Science & Technology (HKUST)
- National Nanyang Technological University
- Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology
- University of Hong Kong
- Tsinghua University
- Fudan University
- City University of Hong Kong
- Peking University
- Chinese University of Hong Kong
Major Glycobiology Associations around the Globe:
- Glyconet Glycobiotechnology Network
- Glycoscience Graduate School
- Mizutani Foundation for Glycoscience
- The Japanese Society of Carbohydrate Research
- Alberta Glycomics Centre
- Copenhagen Center for Glycomics
- CKSP: Center of Know-how for Sugars and Polysaccharides, Ben-Gurion University
- Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry, Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Science
- Glycoprotein Structure/Function Group, Birkbeck College
- Oxford Glycobiology Institute
- University of Liverpool
Conclusion:
International Conference on Glycobiology seeks to bring all scientists, glycobiologists, biochemists, researchers, students, industry experts, delegates, sponsors and exhibitors, together who are involved in field of research and provide a global platform to discuss about their innovation, exchange ideas and interaction with each other.
- Glycobiology and Glycochemistry
- Glycoproteomics Analysis
- Glycoimmunology
- Glycans in Diseases and Therapeutics
- Glycolipids and Glycopeptides
- Mass Spectrometry Analysis
- Glycans in Vaccine Development
- Glycoconjugates, Glycomics and Metabolomics
- Glycoscience and Monosaccharides
- Recent advances in Glycobiology
- Respiratory System
- Digestive System
- Endocrine System
- Reproductive System
- Urinary System
- Nervous System
- Cardiovascular Physiology
- Bones and Joints
- Integumentary System
- Andrology & Gynecology: Current Research
- Journal of Liver: Disease & Transplantation
- Journal of Neuroscience & Clinical Research
- Advanced Biomedical Research and Innovation