
Telemedicine 2018

Theme: Exploring the innovations on Telemedicine and Medical Informatics.
Meetings International proudly announces the “World Congress on Telemedicine & Medical Informatics” which will be held during October 4-5, 2018 at Las Vegas. The theme of conference is “Healthcare and technology a developing future medicine”. Meetings International provides a Global Platform for Medical, Healthcare Professionals Bioinformatics, Chemistry and Biotech Professionals to Exchange Ideas and knowledge.
Track 1: Telemedicine
Telemedicine is the use of telecommunication and information technologies to provide clinical and medical health care at a distance. It helps to eliminate distance barriers and can improve access to clinical services that would often not be consistently available in distant rural communities. It is also used to save lives in critical care and emergency situations. Although there were distant precursors to telemedicine, it is essentially a product of 20th century telecommunication and information technologies. These technologies permit communications between patient and medical staff with both convenience and loyalty, as well as the transmission of medical, imaging and health informatics data from one site to another. It is a process for accurate data collection in digital format and an electronic medical record for data incorporation and remote transmission Telemedicine is a system for automatically flagging and providing feedback for outlier data.
Related Societies and Associations: International society for telehealth and medicine (ISfTeH), European Health Telematics Observatory (EHTO), European Health Telematics Association (EHTEL), Center for Telemedicine Law (CTL), Canadian Society of Telehealth (CST), Australian New Zealand Telehealth Committee (ANZTC), Association of Telehealth Service Providers (ATSP).
Track 2: Telehealth and medicine today
Telehealth presently aligns the clinical, operational, financial, and strategic effectiveness of a telehealth program. It mainly assists healthcare decision makers in launching sustainable telehealth services within clinically integrated healthcare systems Telehealth is a modern form of health care delivery. Telehealth breaks away from traditional medical care delivery by using recent telecommunication systems including wireless methods. Traditional use of telehealth services has been for specialist treatment. Telehealth is not a determined service, but a collection of means to enhance medical care and education delivery.
Related Societies and Associations: The Utah telehealth network(UTN), UK Telehealth care, The Institute for Health Technology Transformation (iHT2), Personal Connected Health Alliance, Georgian Telemedicine Union, Florida Partnership for TeleHealth, Arizona Telemedicine Program.
Track 3: Healthcare technology
Health care technology implies application of formulated knowledge and skills in the form of devices, drugs, medicines, vaccines, procedures and systems developed to solve a health issues and improve quality of lives. This includes the pharmaceuticals, devices, procedures and organizational systems used in health care technology. It encompasses a wide range of healthcare products and mainly used to diagnose, monitor, treat diseases or medical conditions affecting humans. Earlier diagnostic methods, very low invasive treatment options and reductions in hospital stays are the applications of health science which are intended to improve the quality of health care delivered. There are recent trends in health technology and the proliferation of health care is increasing day by day mainly they have also focused on cost reduction. Medical technology may be classified into medical devices, information technology and healthcare services.
Related Societies and Associations: Telemedicine Information Exchange (TIE), Swiss association of telemedicine, Office for the Advancement of Telehealth (OAT), Nordic Telemedicine Association (NTA), National Initiative for Telehealth (NIFTE).
Track 4: Tele-home health
Tele-home health mainly involves at typical day in the life of a home telehealth Patient. Cancer patients often are treated surgically resulting in the need for temporary or permanent ostomies which are surgically created openings in the body for the discharge of body wastes. They utilize inexpensive videophone equipment connecting to the patient’s home through ordinary telephone lines to connect. They mainly include ostomy care, cardiac transplant care, passionate oncology care.
Related Societies and Associations: The office for advancement of telehealth, Telehealth resource centers, Telemedicine Research Center (TRC).
Track 5: Health care communications
Healthcare Communication (IHC) determines the quality of healthcare by optimizing the experience and connecting perception, intelligence and expertise to deliver powerful multichannel communication solutions. This mainly involves the process of healthcare communication through creating and distributing innovative educational schedules and services, advocating for the importance of communication as an essential aspect of clinical care involving in collaborative research on communication in healthcare sector, and partnering with other leading organizations. Healthcare researchers whose area of study involves clinicians who need to initiate new, novel, or unfamiliar topics with their patients; These principles are intended to form the basis for defining standards governing responsible, faithful and deceiving communications to inform health or medical care professionals and payers about the effective use of medicines.
Related Societies and Associations: Alaska Telemedicine Project (ATP), Eastern Montana Telemedicine Network (EMTN), Montana Healthcare Telecommunications Alliance (MHTA), American academy on communication and health care.
Track 6: Digital health care services
Digital health is the linking of genomic and digital technologies with health, healthcare and society to enhance the efficiency of clinical care delivery and make medicines more personalized and precise. It involves the use of information and communication technologies to help address the health problems and challenges faced by patients. These technologies include both hardware and software solutions and services, including email, mobile phones, web-based analysis, and applications, text messages, and clinic or remote monitoring sensors. Generally, digital health is concerned about the development of interconnected health systems to improve the use of computational technologies, smart devices, computational analysis techniques and communication media to aid healthcare professionals and patients manage illnesses and health risks, as well as promote health and wellbeing. Digital health is a multi-disciplinary domain which involves many stakeholders, including clinicians, researchers and scientists with a wide range of expertise in healthcare, engineering, social sciences, public health, health economics and management.
Related Societies and Associations: Global digital health care network, European health telematics association, Global health care technology.
Track 7: Telenursing
Telenursing is the use of communications technology in nursing to enhance patient care. It involved the use of electromagnetic channels such as wires, radio and optical to transmit voice, data and video communications using electrical or optical transmissions between humans or the computer. It involves patient and client interaction through information technology. It is part of telehealth and as well as telemedicine, and has many points of contacts with other medical and non-medical applications, such as tele diagnosis, teleconsultation, and telemonitoring. telenursing is the provision of nursing care to subjects living at remote places using distance communications technology. The tele nurses should have adequate knowledge and skill to support patient needs and make accurate decisions.
Related Societies and Associations: ICN Telenusring Network, International council of nurses, International Council of Nurses Telenursing Network.
Track 8: Medical informatics
Medical informatics is the application of computers, communications and information technology and systems to all fields of medicine - medical care, medical education and medical research. The definition of Medical Informatics is dynamic due to the rapidly changing nature of both medicine and technology the sharing of a variety of information back and forth between people and healthcare entities. Medical Informatics is a new, exciting and evolving field. New specialties and careers are now possible. The expectation is that information technology will improve medical quality, patient safety, educational resources and patient-physician communication, while decreasing cost. Applied Medical Informatics studies the dispensation of medical statistics, the potent, management of information using computer technology, and the impact of such methods on medical research, education.
Related Societies and Associations: American Medical Informatics Association, Association of Medical Diagnostics Manufacturers, Medical Imaging & Technology Alliance (MITA) , Medical Device Manufacturers Association (MDMA) , Hearing Industries Association, Generic Pharmaceutical Association (GPhA).
Track 9: Patient informatics
Patient Informatics is a new aspect of Medical Informatics that largely reflects the empowered healthcare consumer. Patients are aware that many non-healthcare businesses are automating and modernizing their business processes to attract a larger market share. Web portals are web-based programs that patients can access for health services. A web portal can be a standalone program or it can be integrated with an electronic health record. Patient portals began as a web based entrance to a healthcare system for the purpose of learning about a hospital, healthcare system or physician’s practice. Patients would like to have the same automation and convenience of an ATM machine applied to healthcare. Patients are using the Internet as the medical library of choice before and after seeing clinicians. Patient web portals are now available that are standalone or integrated with electronic health records that offer a multitude of patient oriented services.
Related Societies and Associations: American Health Information Management Association, American medical informatics association, Health level seven.
Track 10: Clinical informatics
The application of informatics to the practice of medicine and clinical care Providing clinicians, patients or individuals with knowledge and person-specific or population information, intelligently filtered or presented at appropriate times, to foster better health processes, better individual patient care, and better population health Clinical Informatics is to use modern technologies to advance our ability understand health and health problems, support translational research, develop effective interventions for healthcare delivery. Clinical informatics is so broad and touches so many different aspects of the practice of medicine that each of us comes at it from a slightly different perspective Clinical informaticians use their knowledge of patient care combined with their understanding of informatics concepts, methods, and medical informatics. The information and clinical choice backing included in this field are produced for and utilized by clinicians, patients, and guardians.
Related Societies and Associations: American Nursing Informatics Association,American Standards Testing and Materials.
Track 11: Health system informatics
Health Systems informatics (HSI) is a healthcare consulting firm and mainly focused on delivering high-quality consulting and support services enabling healthcare institutions to meet the ARRA and HITECH requirements through efficient Electronic Medical Record (EMR) accomplishment and optimization resulting in relevant Use. Built on a justification of strapping, diverse, healthcare talent and a “clients as partners” business criteria, HIS was started to provide support in today’s ever-changing healthcare society.
Related Societies and Associations: Canada Health Informatics Association, American Health Information Management Association, Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare, Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society.
Track12: Cancer informatics
Cancer informatics is a multidisciplinary field of medical science that deals with the resources, devices, and methods required to optimize storage, retrieval, acquisition and use of information in the field of cancer research and treatment. Research in cancer biology have seen a dramatic increase in the amount of clinical, medical and research data, in particular with genomic and molecular cancer data. The data can benefit researchers understanding of cancer behavior and development of better therapy and treatment, new and improved data management and analysis tools are needed. Cancer informatics attempts to provide those tools "that interconnect research, clinical activities, and data in an organized and efficient manner, with as broad a database as possible. The coupling of cancer informatics tools with computational modeling and statistical analysis will accelerate the goal of making cancer a more treatable if not curable disease. Cancer informatics mainly helps in management and distribution of annotated molecular data for further research and also for the analysis of an individual tumor to determine its molecular phenotype.
Related Societies and Associations: American society for clinical oncology, The North American association for central cancer registries, American medical informatics association.
Track 13: Medical Informatics research and Services
Medical Informatics application is organized with knowledge and skills in the form of devices, medicines, vaccines, procedures and systems developed to solve a health related problems and improve quality of lives. This includes the pharmaceuticals, devices, instruments, procedures and organizational systems used in health care. The main agenda of social services are to provide better with respect to health services in rural and urban areas. Medical Informatics Research also involves research of proteomes from the level of intracellular protein composition, structure, and its unique activity patterns. It is an important component of functional genomics.
Related Societies and Associations: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, eHealth Initiative, Med Help International The Patient Medical Information Center, NAHDO National Association of Health Data Organizations, National Institute for Health Care Management Research and Educational Foundation.
Track14: Medical Informatics Engineering
Medical Informatics Engineering mainly targets the delivery of medical care over the entire patient care cycle, which includes treatment, medications, monitoring and checkups screening, vaccination, preventive medicine, diagnosis. Model-based decision tools create engineered innovations in clinical operations, individual treatment choice and supporting supply chains to advance safe, high-quality, consistent and accessible healthcare while avoiding unnecessary costs. HSE focuses on the design of engineered processes to combine resources and support clinical decision making to assure its effective implementation over the entire course of a patient’s care.
Related Societies and Associations: Alabama Society for Healthcare Engineering, The Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine, Biomedical and Clinical Engineering Biomedical Engineering Society (BBES).
Meetings International proudly announces the “World Congress on Telemedicine & Medical Informatics” which will be held during November 28-29, 2018 at Las Vegas. The theme of conference is “Healthcare and technology a developing future medicine”. Meetings International provides a Global Platform for Medical, Healthcare Professionals Bioinformatics, Chemistry and Biotech Professionals to Exchange Ideas, Knowledge and Networking at its International Conferences.
Telemedicine meeting 2018 mainly focuses on Telemedicine and medical informatics, It is now being extensively used in medical and health care sectors; Hence telemedicine and medical informatics are expected to grow at a high rate in coming years, which is expected to boost the growth of the medical care technology. Telemedicine is reality today and has come to stay. In Telemedicine one transfers the expertise, not the patient. The term telehealth can refer to clinical and non-clinical services such as medical education and clinical research and telemedicine refers only to the provision of medical services.
Why to attend???
Join your peers around the world focused on learning about Telemedicine and Medical informatics and related advances, which is your single best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the Telemedicine and Medical Informatics community, conduct demonstrations, distribute information, meet with current and potential professionals, make a splash with a new research works, and receive name recognition at this 2-day event. World-renowned speakers, the most recent research, advances, and the newest updates in Telemedicine and Medical informatics are hallmarks of this conference.
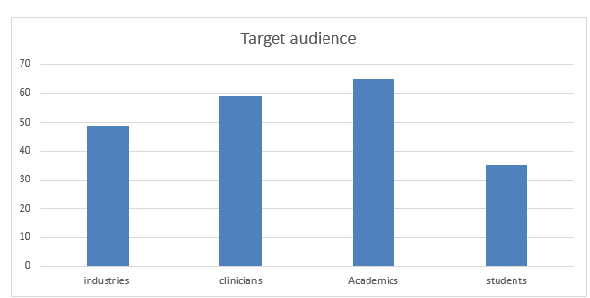
Target Audience:
· Directors/Managers and Business Delegates, Medical specialist.
· Doctors, Nurses, Pharmacist, Director of Laboratories.
· Medical Industries, Investigators, Telemedicine researchers, Post-Doctoral Fellows.
· Research and Diagnostic Laboratories, Clinical Fellows, Students.
· Medical Research companies, Medicine and Pharmacy companies.
· Health policy makers, clinicians and healthcare professionals, health informaticians.
· Physician, Health researchers.
Summary:
The use of information and communication technology to deliver medical services and information from one location to another is telemedicine. Telemedicine can be seen as a way of distributing medical expertise and services to medically underserviced areas such as remote and rural areas using Information technology as a communication platform. For more than 30 years, clinicians, health services researchers, and others have been investigating the use of advanced telecommunications and computer technologies to improve health care. At the intersection of many of these efforts is telemedicine—a combination of mainstream and innovative information technologies. The science of analysis, documentation control and synthesis of information processes within the health care delivery system especially in environment and medical practice is medical informatics. Telemedicine is utilized by health providers in a growing number of medical specialties.Telemedicine consists teledermatology, teleradiology, telecardiology, telepsychiatry and home health care. Telemedicine is reality today and has come to stay. In Telemedicine one transfers the expertise, not the patient. The term telehealth can refer to clinical and non-clinical services such as medical education and clinical research and telemedicine refers only to the provision of medical services.
The future of Telemedicine and Medical informatics is mainly accessible to under-served rural and urban populations and is easy and quick access to specialists. Telemedicine mainly adds thousands of skilled specialists to the healthcare team. Telemedicine is the developing future medicine with improving the medical science and medical care technology.
Importance & Scope:
Telemedicine and medical informatics is now being extensively used in medical and health care sectors;Thus telemedicine and medical informatics are expected to grow at a high rate in coming years, which is expected to boost the growth of the medical are technology.83% of healthcare organizations responded to American Telemedicine Association. They are likely to invest in telehealth with operational efficiency and convenience in mind. 171 healthcare executives participating in the annual ATA Executive Leadership Survey, 88% are likely to purchase telehealth tools by 2017. In 2013 the m health valued at $ 2.4 billion in global revenues.it is estimated that by 2018 it will reach $21.5 billion. By 2018 the Europe will be the largest m health market worth $7.1 billion with the highest predicted growth per year at 61.6%. Over 300 studies have been completed over the past 5 years.
Why Las Vegas?
Global Telemedicine and Medical Informatics Market Share by Country
Why to attend???
Meet Your Target Market With recent business reports on Telemedicine and Health care making news which manifests the tremendous growth in market value for Medical field till 2019. Since Telemedicine and Medical informatics interrelated with sciences like Telehealth, Health informatics, Tele homehealth, Cancer informatics, Biomedical informatics it would be a great opportunity for companies dealing with Analytical instruments useful in these fields. Also many upcoming students and researchers can benefit themselves by participating world class International workshops, symposia during the conference which will be conducted by experts in the respective fields.
Major telemedicine and medical informatics Related Associations around the Globe:
National Association for Biomedical Research (NABR)
Alabama Society for Healthcare Engineering,
Biomedical Engineering Society (BMES)
American Statistical Association (ASA)
American Medical Informatics Association
Generic Pharmaceutical Association (GPhA)
American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering
American Society for the Advancement of Pharmacotherapy (ASAP)
National Community Pharmacists Association (NCPA)
Academy of Managed Care Pharmacy (AMCP)
American Society of telemedicine
Drug Information Association
The Japanese Society of Pharmacognosy (JSP)
American Society of Consultant Pharmacists
Major telemedicine and medical informatics Related Research Units in Hong Kong:
Hong Kong telemedicine association
China medical informatics association
Hong Kong society for medical informatics
Hong Kong academy of medicine
Target Audience:
Directors/Managers and Business Delegates, Medicine specialist, Doctors, Nurses, Pharmacist, Director of Laboratories, Universities, Industries, Investigators, telemedicine researchers, Post-Doctoral Fellows, Research and Diagnostic Laboratories, Clinical Fellows, Students, medical Research companies, Medicine and Pharmacy companies.
Rise in the number of clinical trials and health awareness for medical devices, rapid growth of research analysis software and solutions, and use of telemedicine as tool for the growth of the market.
Glance at Market of Telemedicine and Medical informatics:
The market is mainly driven by the increasing research funding for Telemedicine and Medical informatics from governments and private investors, growing demand for digital health care in the U.S. and Europe, and the increasing need for medical technology. However, low adoption rates and data complexity inhibits the growth of the Medical care market to a certain extent. Telemedicine is used extensively in health and clinical field. Thus, the rapid growth experienced by Medical informatics sector is assisting the growth of the Medical field.
In the year 2015, the telemedicine market was estimated to be worth around USD 23,224 million and is expected to reach USD 66,606 million by the year 2021, growing at a CAGR of 18.8% during the forecast period (2017-2022). The Global Telemedicine Market is poised to grow at a CAGR of around 16.3% over the next decade to reach approximately $78.3 billion by 2025.
Statistics which shows growth in importance of Telemedicine and Medical informatics:
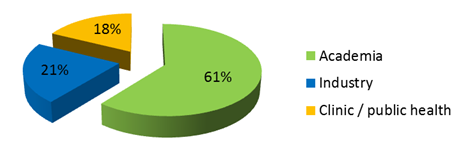
Statistics of Industries Associated with Telemedicine and Medical informatics:
Asia pacific was the market leader with a good share of the global market, followed by Europe and united states. The presence of a large number of analytical equipment manufacturers has contributed significantly to the United states and European medical market. However, the Asia-Pacific region represents a significant growth opportunity for the Telemedicine market during the forecast period of 2014 to 2018. The APAC market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 23% during the forecast period. The growth in this market is driven by the growing telemedicine and health care field
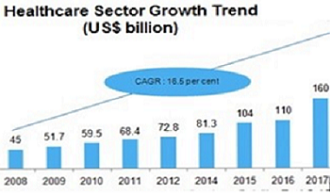
Fund Allotment towards Telemedicine and Medical Informatics Research:
The National Institutes of Health has provided millions of dollars in new funding to support Comprehensive Telemedicine Centres at Mayo Clinic, the United states, and the University of Florida. Some of the digital health companies are Maxwell health, health line media, pear therapeutics and Cala health.
These centres will receive an estimated $9 million to $10 million each over the next five years to create resources and initiate research programs that will ramp up the national Health science capabilities. Overall, the full global telehealth market is forecast to be worth $43 billion by 2019, compared to the estimated value of $16 billion by the end of 2013. The growth is the fact that a survey of 140 large employers in the United States revealed that 48% of them already offered access to services from the top telehealth companies to their employees and 74% are expected to offer that by the end of 2016.
Teladoc is one of the largest providers of telemedicine service
MDlive it has grown very quickly and has already raised more than $70 million in investment.
Spruce Health has raised $17 million in investment, mainly from its most recent $15 million series A in March 2015 that included top investors like Kleiner Perkins and Google Ventures.
- Telemedicine
- Telehealth and medicine today
- Healthcare technology
- Tele-home health
- Health care communications
- Digital health care services
- Telenursing
- Medical informatics
- Patient informatics
- Clinical informatics
- Health system informatics
- Cancer informatics
- Medical Informatics research and Services
- Medical Informatics Engineering
- Journal of Health & Medical Informatics
- Journal of Applied Bioinformatics & Computational Biology
- Journal of Health Informatics & Management
8 Organizing Committee Members
6 Renowned Speakers
Chris Boone
Real World Informatics and Strategies. Avalere Health, an Inovalon Company
USA
USA
Ronald R. O’Donnell
Arizona State University College of Health Solutions
USA
USA
Petra Perner
Institute of Computer Vision and
applied Computer Sciences
Germany
Vivian Vimarlund
Linkoping university
Sweden
Sheri Brynard
Lettie Fouche School
South Africa
K Ganapathy
Dr MGR Tamilnadu Medical University
India






































































































































